THE ROLE OF ENDANGERED LANGUAGES IN PRESERVING CULTURAL HERITAGE
October 7, 2024
Language is essential for maintaining and passing down cultural identity, acting as a vibrant and complex medium through which communities express and sustain their shared values, traditions, and stories. Endangered languages play a crucial role in preserving cultural heritage, as they embody the unique worldviews, traditions, stories, and practices of the communities that speak them.
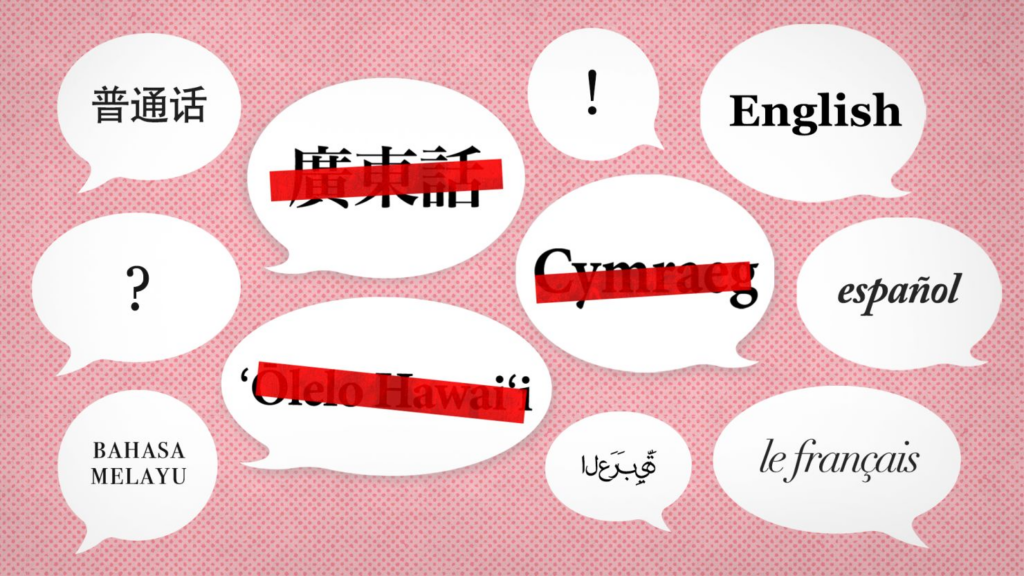
Here are several key points that highlight the significance of endangered languages in cultural preservation:
1. Cultural Identity
Endangered languages are integral to the identity of their speakers. They carry cultural nuances, values, and philosophies that define a group’s way of life. When a language disappears, a significant part of the community’s identity often vanishes with it.
2. Oral Traditions and Stories
Many endangered languages are carriers of oral traditions, folklore, and histories passed down through generations. These stories often encompass knowledge about the land, ancestors, spirituality, and communal practices that are not documented in written form. The loss of a language can mean the loss of these vital narratives.
3. Unique Knowledge Systems
Languages often encode unique ecological knowledge and local practices. Indigenous languages can include specific terms for local flora and fauna, traditional ecological wisdom, and sustainable practices that are integral to the survival of the community. Protecting these languages is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and local knowledge systems.
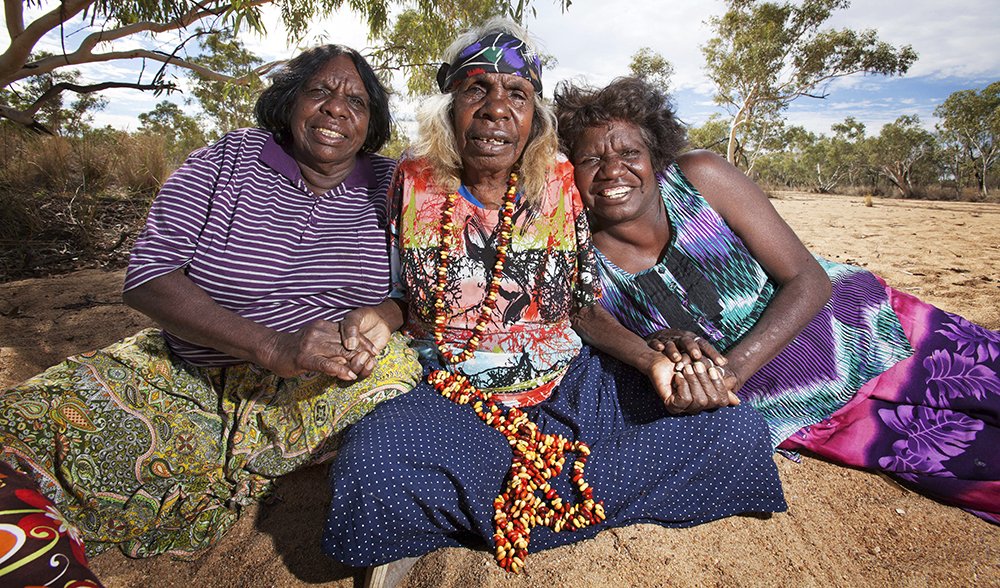
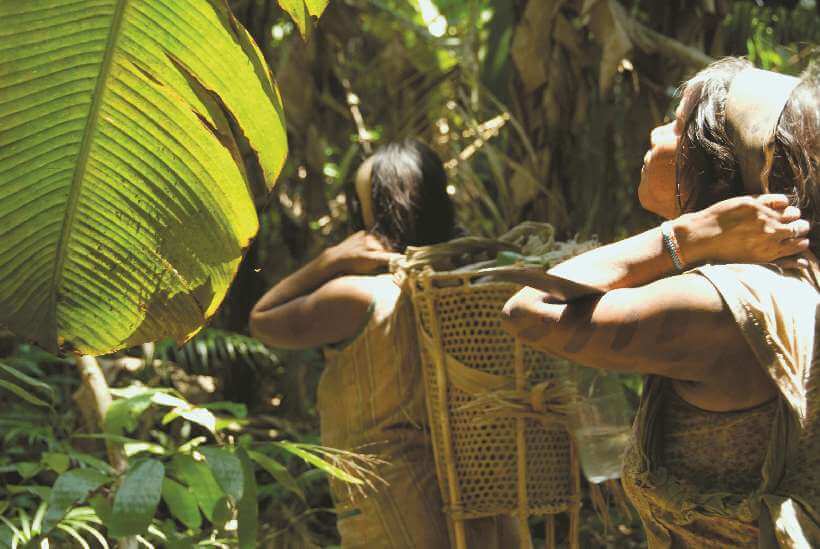
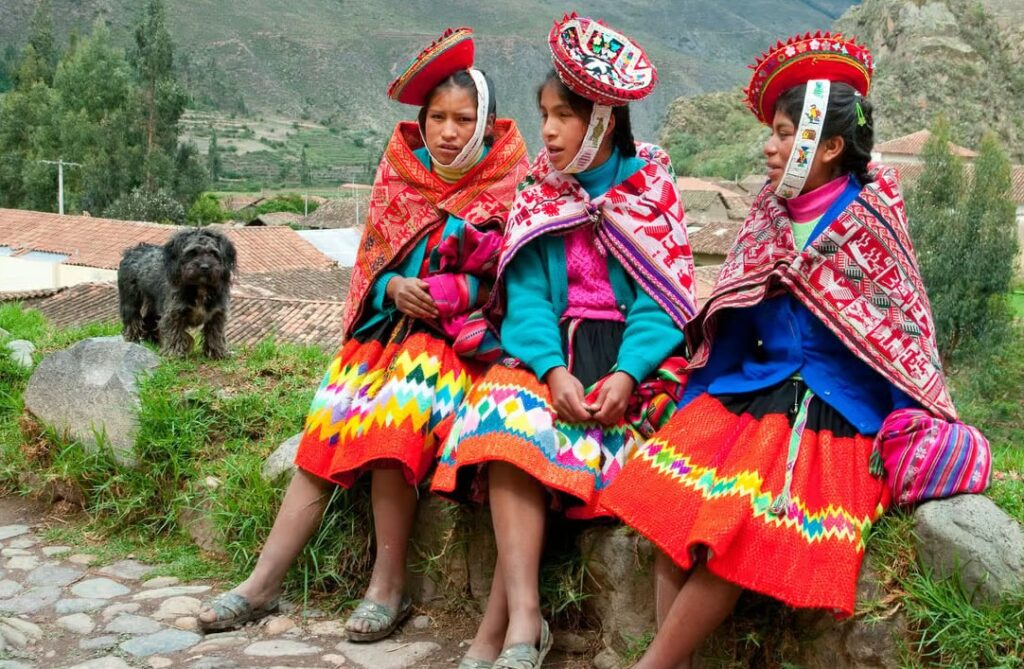



4. Rituals and Practices
Many cultural rituals, songs, and ceremonies are tied to specific languages. Language provides the framework for expressing cultural practices, whether in religious ceremonies, celebrations, or communal gatherings. The erosion of a language can lead to the weakening or disappearance of these practices.




5. Community Empowerment
Language revitalization efforts can empower communities by fostering a sense of pride and ownership over their cultural heritage. Engaging in language preservation can unite communities, encouraging collaboration and increasing awareness of their cultural significance.
6. Educational Resources
There is potential for developing educational resources in endangered languages. Schools and community initiatives that use local languages in teaching can not only help revitalize the language but also reinforce cultural identity and heritage among younger learners.
7. Global Biodiversity and Cultural Diversity
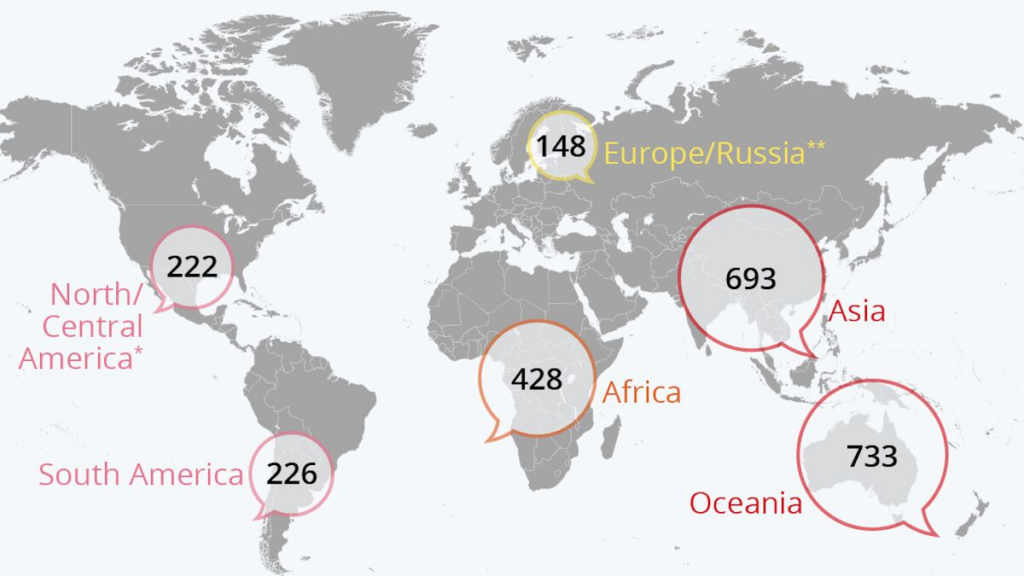
The extinction of languages often parallels the reduction of biodiversity. Globally, there is an increasing recognition that cultural diversity is as important as biological diversity. Protecting endangered languages supports both cultural heritage and ecological sustainability. The languages that are nearing extinction play a vital role in shaping the identities of their communities, contributing significantly to the rich diversity of our global society.

The loss of endangered languages equates to the loss of diverse worldviews and cultural heritage. As such, their preservation is essential not only for the communities that speak them but for humanity as a whole.
Efforts aimed at revitalizing and maintaining these languages contribute to the broader goals of cultural sustainability and intergenerational knowledge transfer. In this context, safeguarding endangered languages becomes both a moral and practical imperative in nurturing the rich tapestry of human diversity.
Nilufar Jalilova
4th Year Student, International Journalism Faculty
Uzbekistan State World Languages University, UZSWLU

No Comments so far
Jump into a conversationNo Comments Yet!
You can be the one to start a conversation.