
Although play is often seen as a simple pastime, it actually plays a crucial role in the growth and learning of young children. Children play from the moment they are born, and this innate desire is a valuable tool that influences their physical, social, emotional, and cognitive growth. Comprehending the diverse functions of play can assist parents, educators, and caregivers in establishing stimulating surroundings that promote comprehensive development. Play may be a foundation of early childhood instruction, serving as necessarily portion of the instructive prepare that cultivates development over different spaces.
Cognitive Development
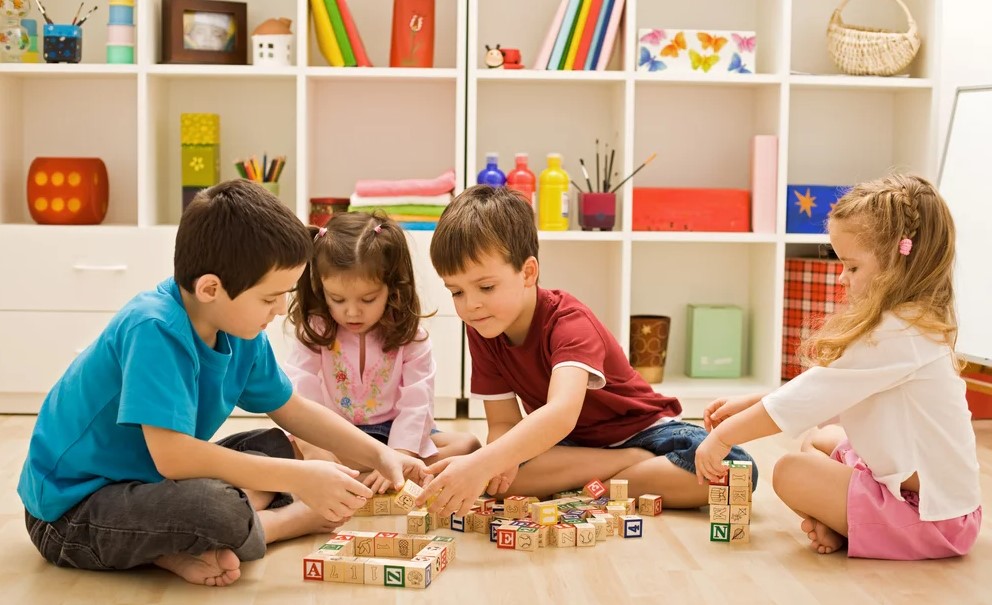
Early childhood cognitive development is largely dependent on play. Children learn to solve problems, experiment with new ideas, and explore their surroundings via play. Playing pretend, building with blocks, or playing easy games are examples of activities that promote critical thinking and increase brain activity.
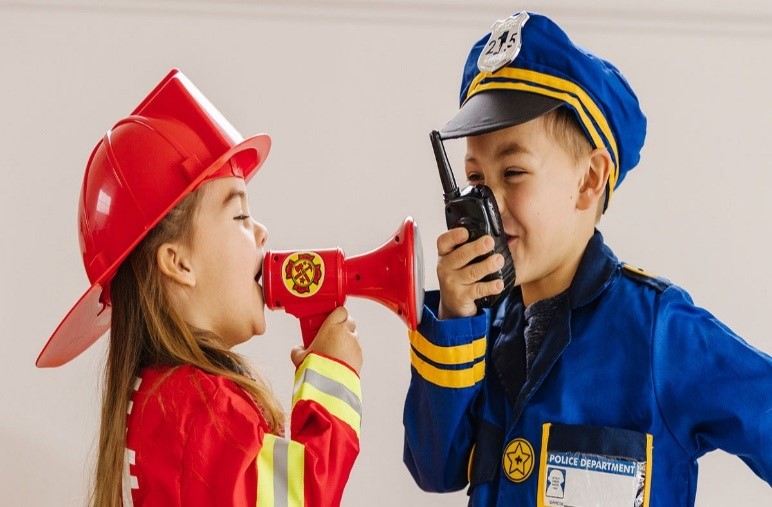


For example, children who play imaginatively are not only acting out scenarios. They are also sharpening their language skills, improving their memory, and developing their planning and organizing abilities. Studies reveal that kids who participate in various play activities have better academic outcomes as adults.
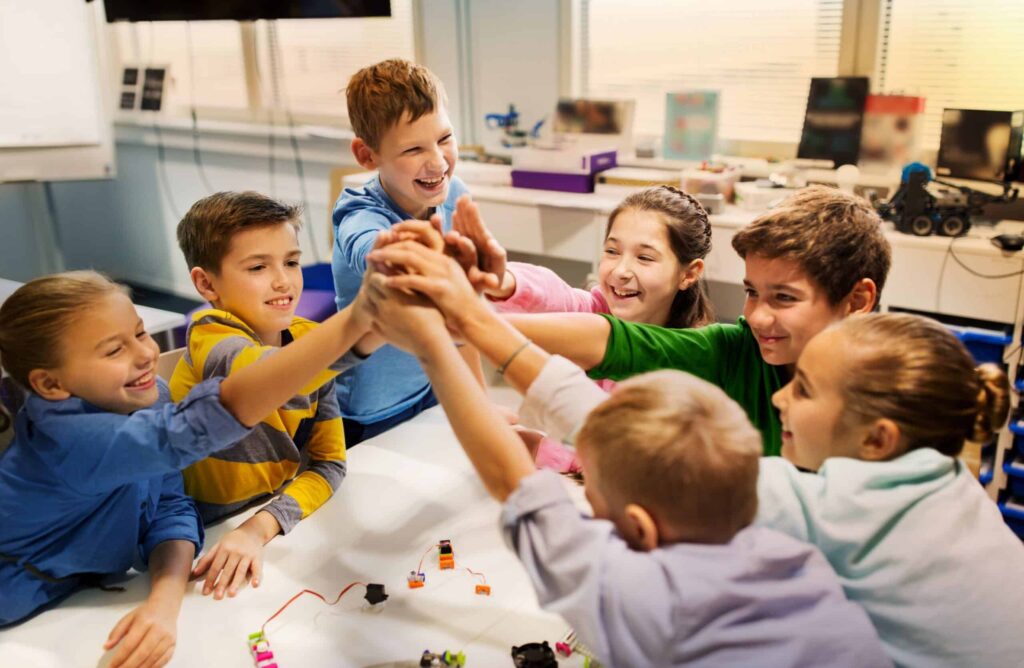
Social Skills
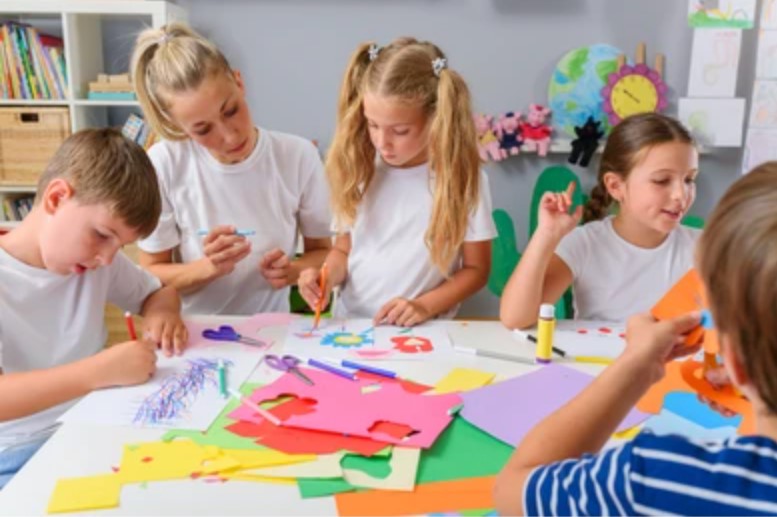
Play is a vital time for social contact and the development of interpersonal skills. Children learn to compromise, share, take turns, and handle conflict as they play together. As kids, negotiate connections with peers, these exchanges aid in their understanding of social norms and the development of empathy.
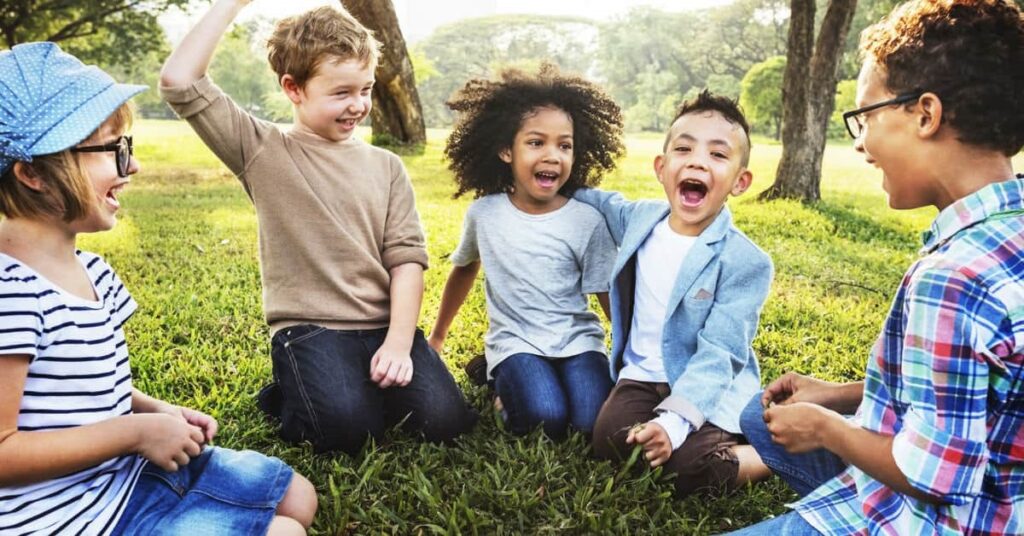
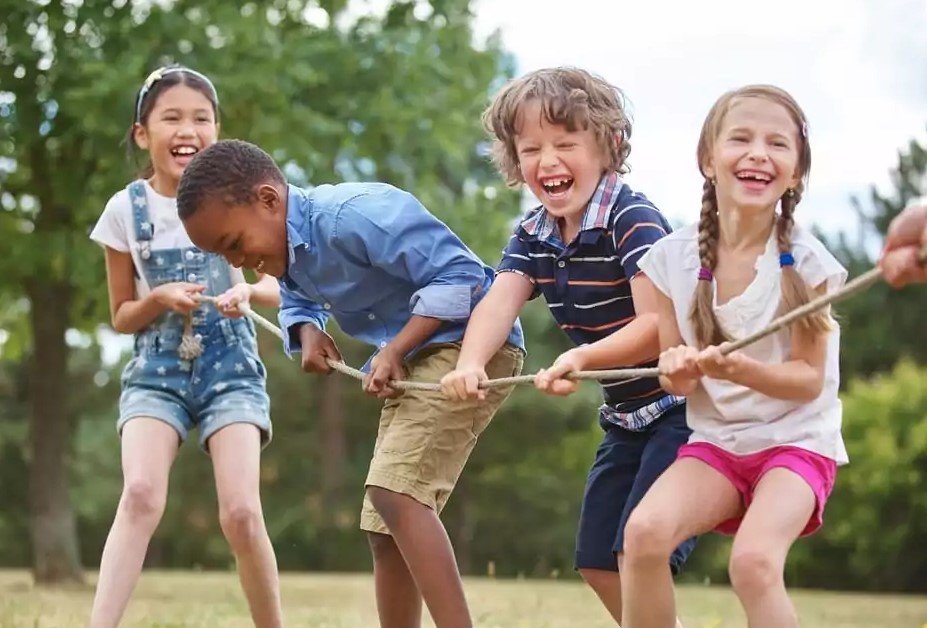


Playing games in groups, whether they are organized or unstructured, promotes collaboration and team spirit. Effective communication of thoughts and feelings is something that children learn, and it sets the foundation for lifelong healthy relationships.
Emotional development
Children can express their feelings and learn self-control in a safe environment through play. Children can safely explore difficult emotions like fear, excitement, and grief through role-playing or storytelling. They are able to understand their feelings and create coping mechanisms due to this exploration.
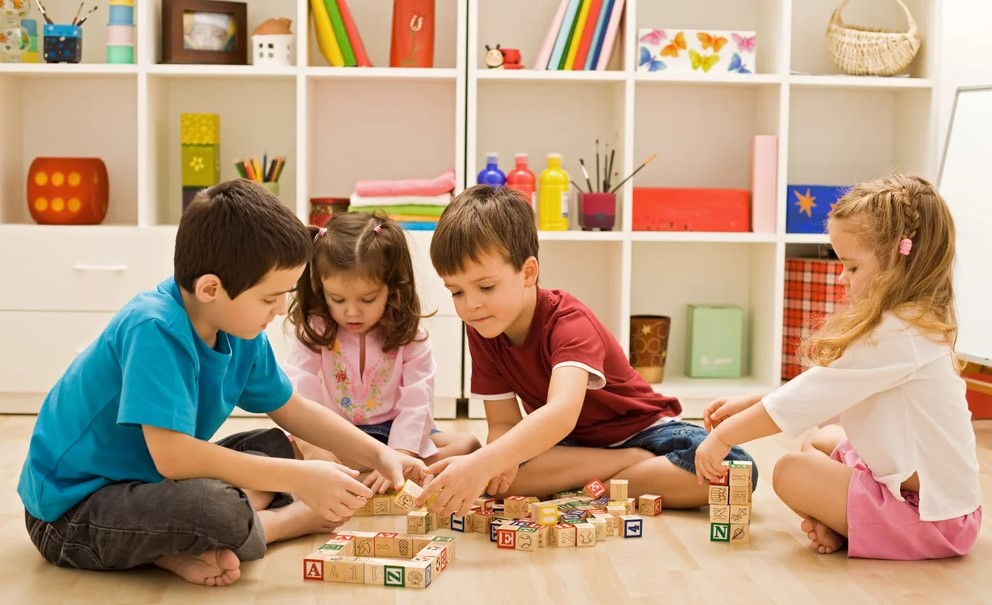
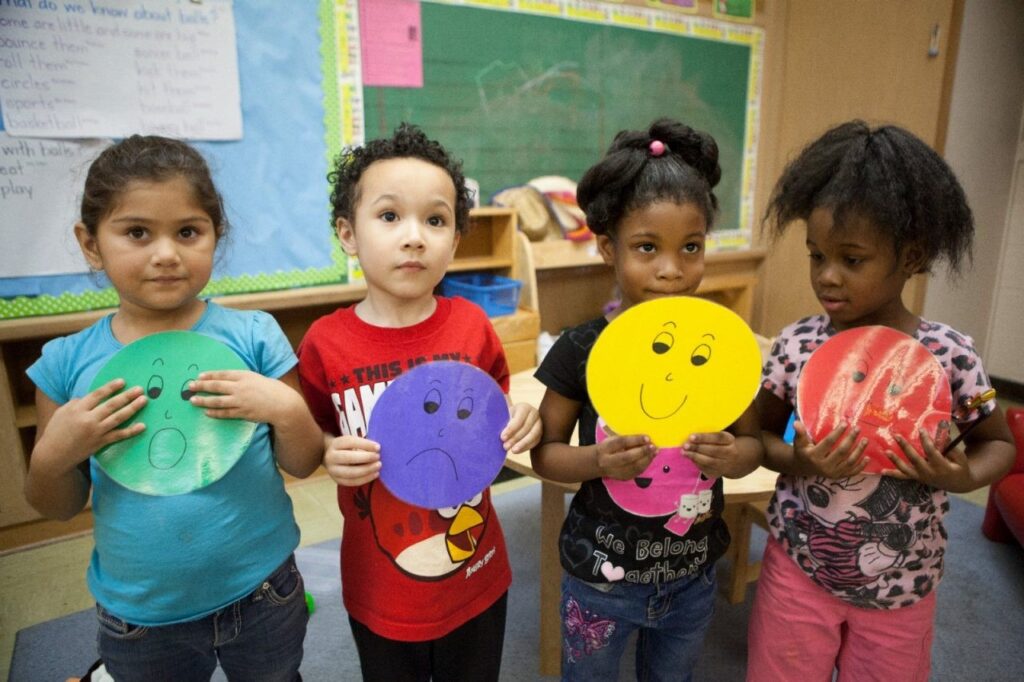



Play also helps people become more resilient. Children gain perseverance and adaptability skills when they face difficulties during play, such as losing a game or having to overcome a challenging hurdle. Resilience in the face of adversity is essential to emotional health.
Physical development
Playing outside is crucial for improving motor skills and general health. Running, jumping, climbing, and ever-easy sports like to improve strength, balance, and coordination. While activities that use little objects, such as cutting, drawing, or building, can help to develop fine motor abilities.
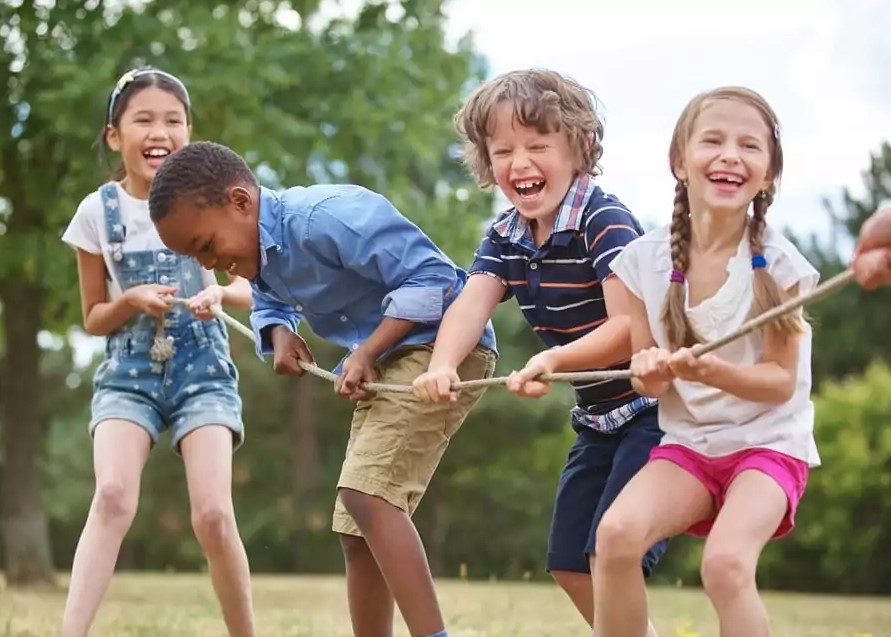
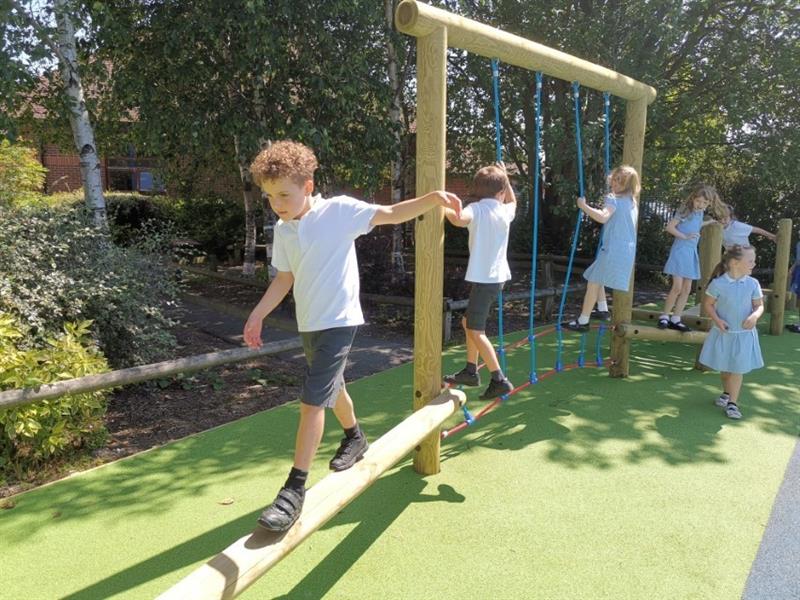




Additionally, active play lowers the risk of obesity and promotes exercise, all of which are beneficial to physical health. In a time when more people are leading inactive lives, promoting physical play is essential to creating healthy, wellness-focused lifelong behaviors.
Creativity and imagination
Play is a natural catalyst for creativity. When children engage in creative play, they use their imagination and creativity to create unique situations and solutions. This imaginative power is important not only for artistic expression but also for innovative work to solve problems.



Creativity that drives different thinking—the ability to come up with multiple solutions to a problem—is a critical skill in a rapidly changing world.
Conclusion
The part of play in early childhood cannot be exaggerated. It could be a crucial fix in a child’s advancement over numerous spaces. As guardians and teachers recognize the significance of play, they can make situations that prioritize perky learning encounters.
By giving openings for changed sorts of play – cognitive, social, physical, and creative – adults can bolster children in becoming well-rounded people prepared with the aptitudes essential to explore the complexities of life. Eventually, grasping the control of play not as it were enhances childhood but lays a solid establishment for future victory and well-being. Consolidating play into early childhood instruction is crucial for cultivating all-encompassing improvement and preparing children with basic life abilities that will benefit them all through their lives.
Dilnoza Qodirova
4th Year Student, International Journalism Faculty
Uzbekistan State World Languages University, UZSWLU

No Comments so far
Jump into a conversationNo Comments Yet!
You can be the one to start a conversation.